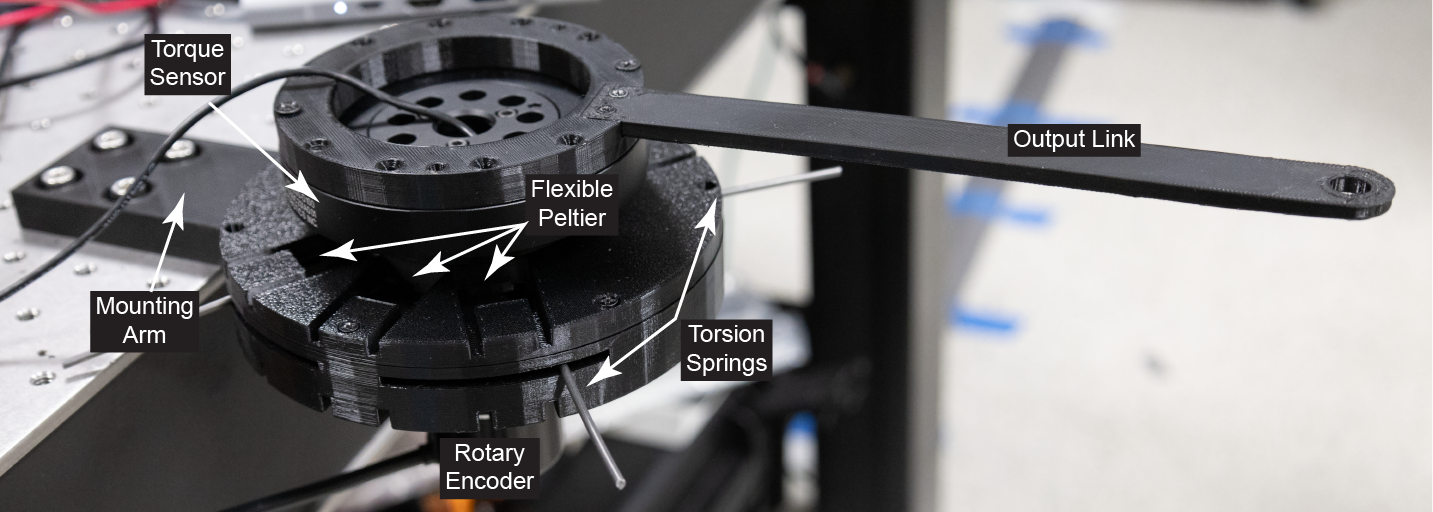
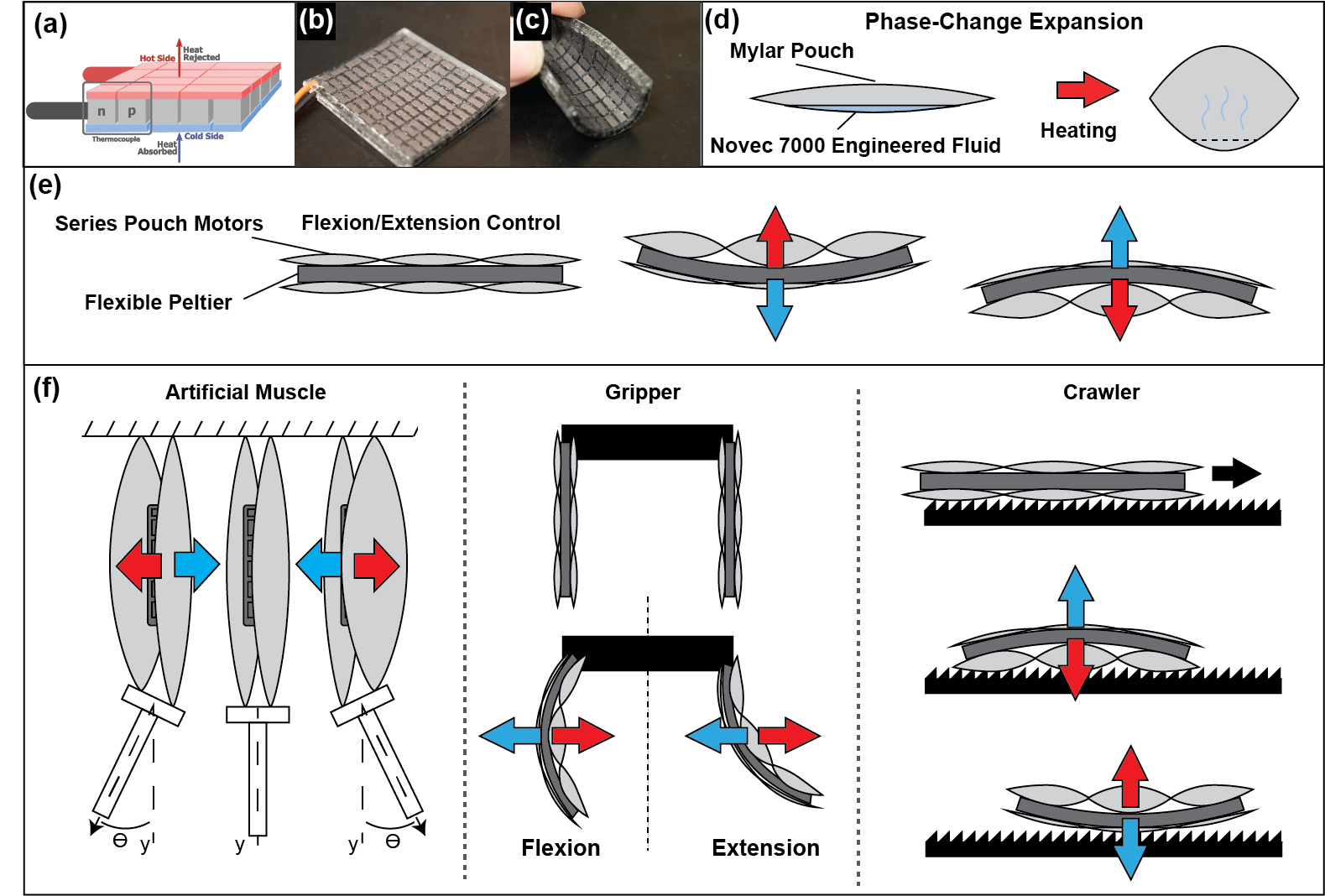
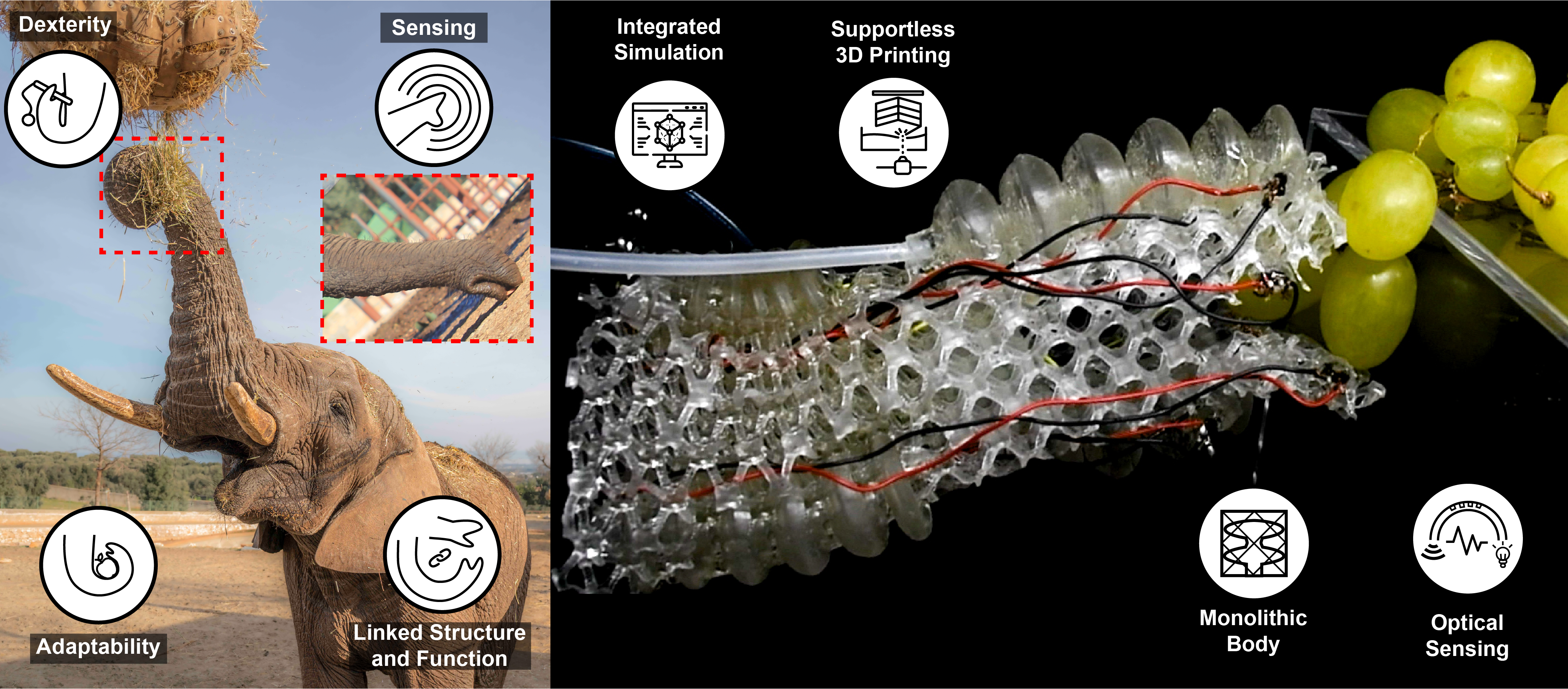
Predicting UPDRS Motor Symptoms From Force Plates Using Machine Learning
2024
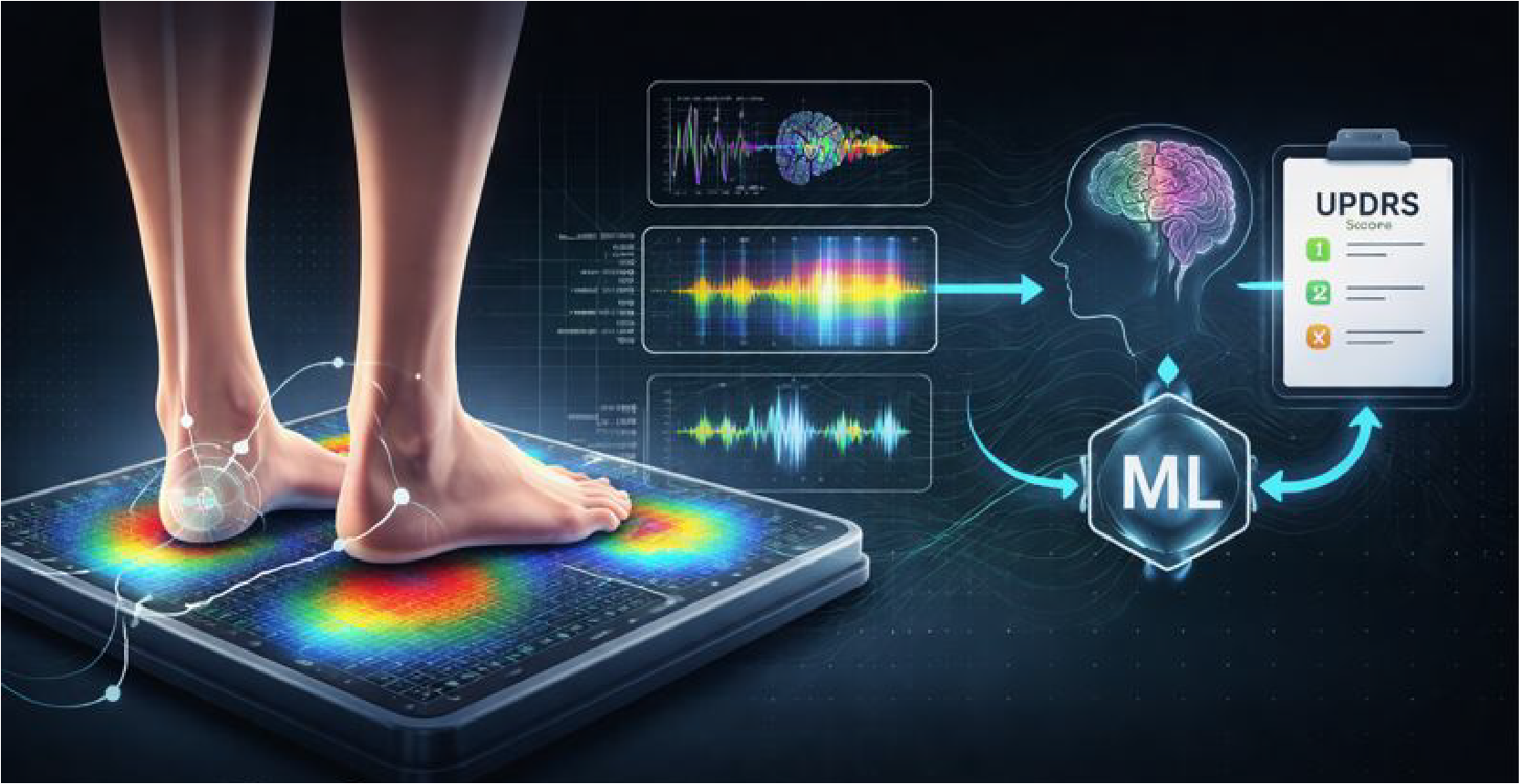
Force-plate signals → interpretable features and models to estimate UPDRS motor symptom severity.
I’m a postdoctoral researcher at the Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT) in Genova. I build thermo-active soft robotic systems and investigate sensing + control for compliant manipulation.